|
|


 Alan Turing
Alan Turing
|
|
People & Pop Culture
Alan Turing was found dead at age 42. He had published his seminal paper,
"On Computable Numbers," in 1936, as well as posing significant
questions about judging "human intelligence" and programming and
working on the design of several computers during the course of his career.
A mathematical genius, Turing proved instrumental in code-breaking efforts
during World War II. His application of logic to that realm would emerge
even more significantly in his development of the concept of a "universal
machine."

|
|
|
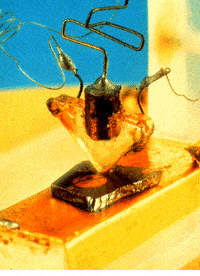 Junction transistor
Junction transistor
|
|
Components
A silicon-based junction transistor, perfected by Gordon Teal of Texas
Instruments Inc., brought the price of this component down to $2.50. A Texas
Instruments news release from May 10, 1954, read, "Electronic
"brains" approaching the human brain in scope and reliability came
much closer to reality today with the announcement by Texas Instruments
Incorporated of the first commercial production of silicon transistors
kernel-sized substitutes for vacuum tubes."
The company became a household name when the first transistor radio
incorporated Teal's invention. The radio, sold by Regency Electronics for $50,
launched the world into a global village of instant news and pop music.

|
|
|
 IBM 650
IBM 650
|
|
Computers
The IBM 650 magnetic drum calculator established itself as the first
mass-produced computer, with the company selling 450 in one year. Spinning at
12,500 rpm, the 650's magnetic data-storage drum allowed much faster access to
stored material than drum memory machines.

|

|
|

|
|
